Category Archives: Journal Article
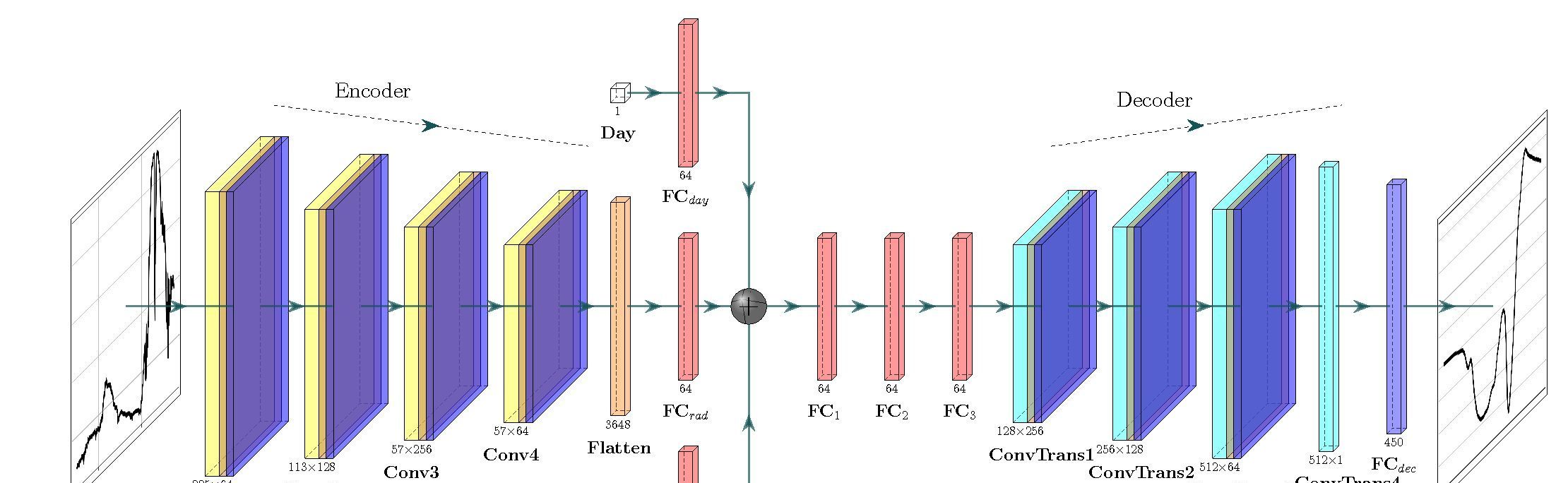
Atmospheric correction of vegetation reflectance with simulation-trained deep learning for ground-based hyperspectral remote sensing
We propose a framework for obtaining the vegetation spectral reflectance from at-sensor spectral radiance, which relies on a time-dependent Encoder-Decoder Convolutional Neural Network trained and tested using simulated spectra generated from radiative transfer modeling.
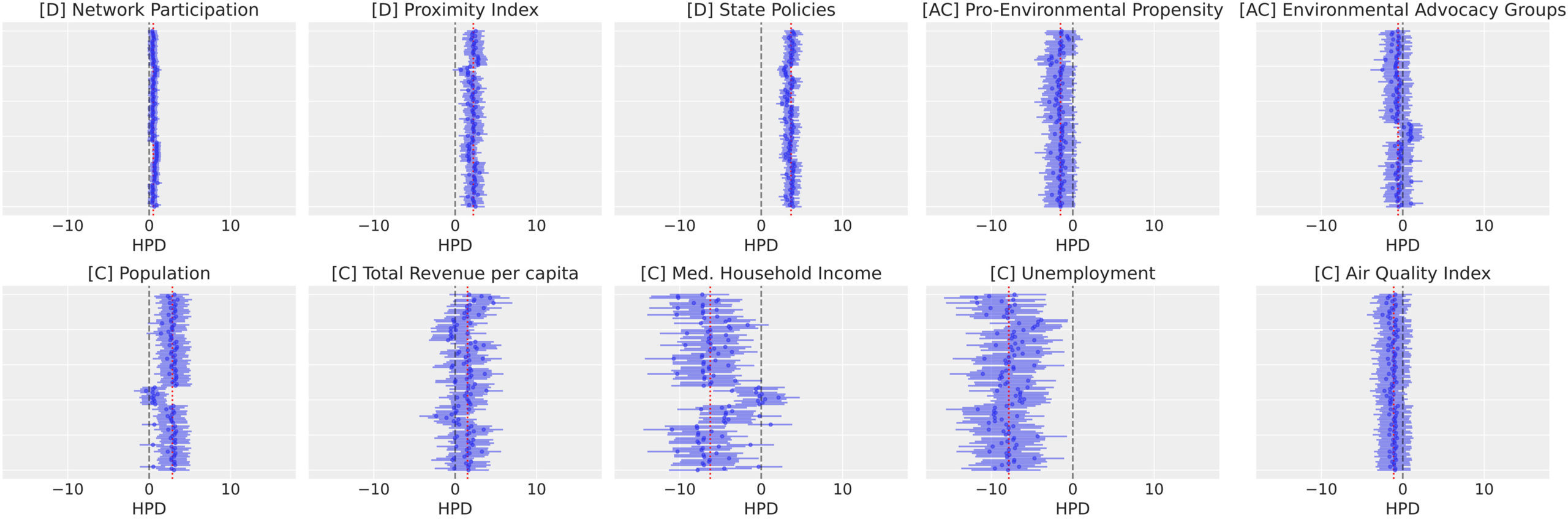
Covariance in policy diffusion: Evidence from the adoption of hyperlocal air quality monitoring programs by US cities
In this work, we explore the influence of multiple diffusion mechanisms: learning, imitation, and coercion; policy mobility factors; and internal determinants on the likelihood of hyperlocal air quality monitoring program (HAMP) adoption by large cities in the US with a population >300,000 over the past decade.
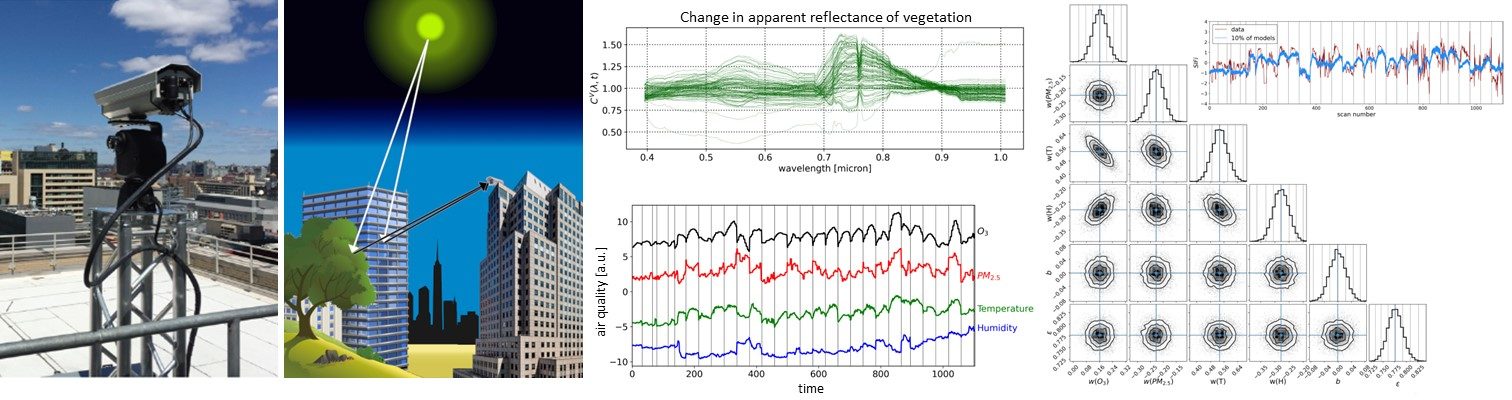
The Impacts of Air Quality on Vegetation Health in Dense Urban Environments: A Ground-Based Hyperspectral Imaging Approach
We examine the impact of changes in ozone (O3), particulate matter (PM2.5), temperature, and humidity on the health of vegetation in dense urban environments, using a very high-resolution, ground-based Visible and Near-Infrared (VNIR, 0.4–1.0 μm with a spectral resolution of 0.75 nm) hyperspectral camera deployed by the Urban Observatory (UO) in New York City.
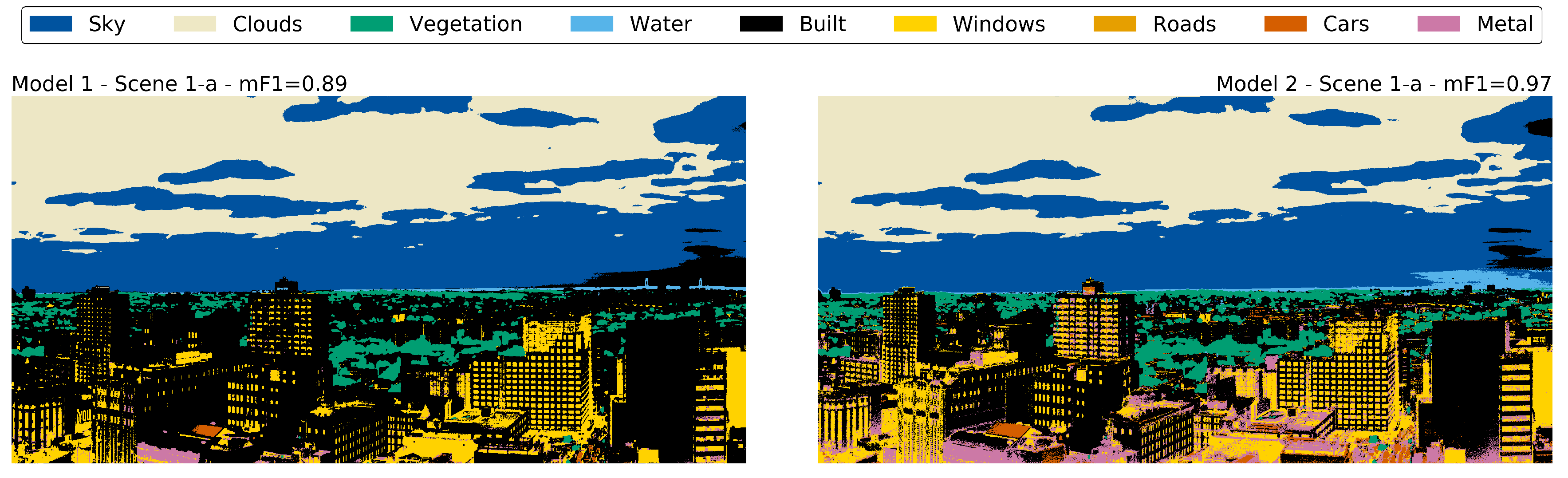

Pixel-Wise Classification of High-Resolution Ground-Based Urban Hyperspectral Images with Convolutional Neural Networks
Using ground-based, remote hyperspectral images from 0.4–1.0 micron in ∼850 spectral channels—acquired with the Urban Observatory facility in New York City—we evaluate the use of one-dimensional Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for pixel-level classification and segmentation of built and natural materials in urban environments.

Galaxy pairs in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey – XI. A new method for measuring the influence of the closest companion out to wide separations
We describe a statistical approach for measuring the influence that a galaxy’s closest companion has on the galaxy’s properties out to arbitrarily wide separations.
