The Effects of Atmospheric Modeling Covariance on Ground-Based Hyperspectral Measurements of Surface Reflectance
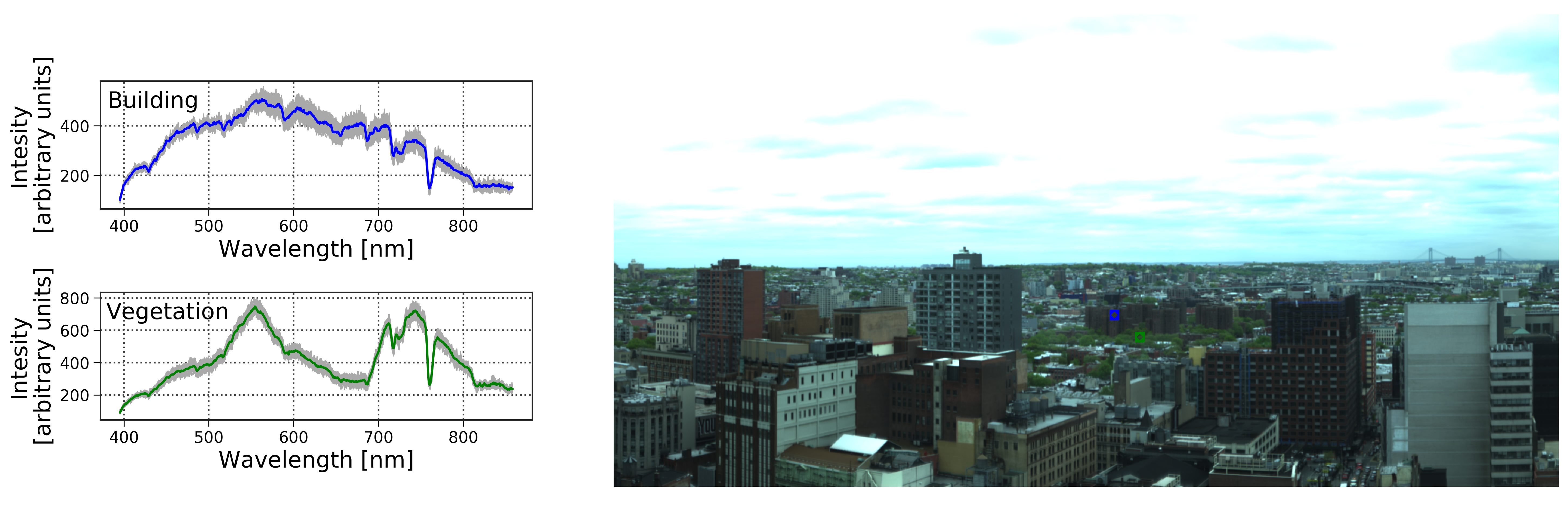
This paper presents a novel framework for estimating the covariance and uncertainties of atmospheric parameters and the reflectance spectra of urban surfaces in high-resolution ground-based hyperspectral images. By integrating open source software for atmospheric modeling and statistical sampling, we demonstrate the use of Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) sampling to quantify the full posterior distributions in a joint fit of both molecular concentrations for atmospheric attenuation and parameterized surface reflectance to spectroscopic observations of an urban scene. We present a use case at visible and near-infrared wavelengths (0.4-1.0 micron) in ∼850 spectral channels where the uncertainty in atmospherically corrected surface reflectance of vegetation in the scene is acquired by propagating the uncertainties obtained from modeling the reflectance of a nearby building surface.
